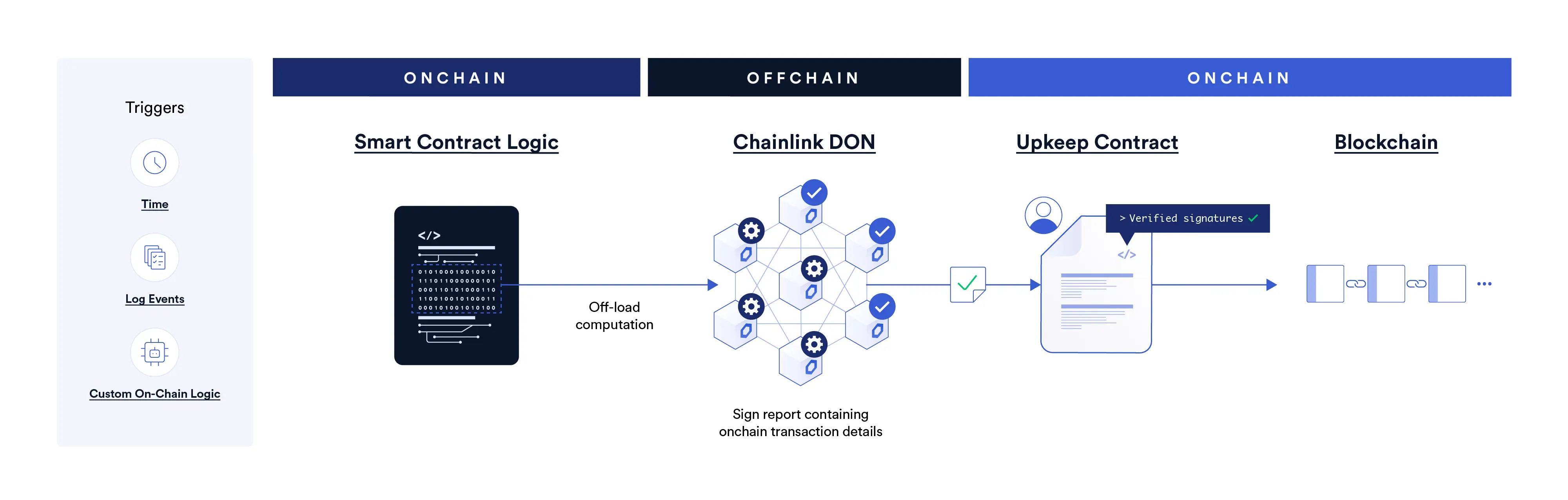
Chainlink Automation là một dịch vụ phi tập trung bao gồm một số nodes lắng nghe một số sự kiện cụ thể và khi được kích hoạt, nó sẽ thực thi một số hàm quan trọng của smart contract một cách tự động.
Concepts
Trong chainlink, ta gọi một action cần thực thi là upkeep và điều kiện thực thi là trigger. Hiện tại Chainlink hỗ trợ 3 loại trigger:
- Time-based trigger
- Custom logic trigger
- Log trigger
Create Automation-Compatible Contracts
Có thể follow theo Video: Smart Contract Lottery - Introduction to Chainlink Automation - Foundry Fundamentals để hiểu cách tạo ra một automation cơ bản. Xem contract mẫu tương thích với interface AutomationCompatibleInterface ở đây.
Về cơ bản, để contract có thể được tự động hóa việc thực thi hàm bởi Chainlink Automation, ta cần import và implement các phương thức của interface AutomationCompatibleInterface:
import {AutomationCompatibleInterface} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/automation/AutomationCompatible.sol";interface AutomationCompatibleInterface {
/**
* @notice method that is simulated by the keepers to see if any work actually
* needs to be performed. This method does does not actually need to be
* executable, and since it is only ever simulated it can consume lots of gas.
* @dev To ensure that it is never called, you may want to add the
* cannotExecute modifier from KeeperBase to your implementation of this
* method.
* @param checkData specified in the upkeep registration so it is always the
* same for a registered upkeep. This can easily be broken down into specific
* arguments using `abi.decode`, so multiple upkeeps can be registered on the
* same contract and easily differentiated by the contract.
* @return upkeepNeeded boolean to indicate whether the keeper should call
* performUpkeep or not.
* @return performData bytes that the keeper should call performUpkeep with, if
* upkeep is needed. If you would like to encode data to decode later, try
* `abi.encode`.
*/
function checkUpkeep(bytes calldata checkData) external returns (bool upkeepNeeded, bytes memory performData);
/**
* @notice method that is actually executed by the keepers, via the registry.
* The data returned by the checkUpkeep simulation will be passed into
* this method to actually be executed.
* @dev The input to this method should not be trusted, and the caller of the
* method should not even be restricted to any single registry. Anyone should
* be able call it, and the input should be validated, there is no guarantee
* that the data passed in is the performData returned from checkUpkeep. This
* could happen due to malicious keepers, racing keepers, or simply a state
* change while the performUpkeep transaction is waiting for confirmation.
* Always validate the data passed in.
* @param performData is the data which was passed back from the checkData
* simulation. If it is encoded, it can easily be decoded into other types by
* calling `abi.decode`. This data should not be trusted, and should be
* validated against the contract's current state.
*/
function performUpkeep(bytes calldata performData) external;
}Hàm checkUpkeep sẽ được thực thi off-chain (simulate) nhằm kiểm tra xem có nên gọi hàm performUpkeep hay không. Nếu biến boolean trả về của checkUpkeep là true thì performUpkeep sẽ được thực thi.
Hàm này có thể dùng on-chain data thông qua tham số checkData. Kết quả của việc tính toán (giá trị trả về của checkUpkeep) sẽ được gửi đến tham số performData của performUpkeep.
Một implementation ví dụ của checkUpkeep:
function checkUpkeep(
bytes calldata /* checkData */
)
external
view
override
returns (bool upkeepNeeded, bytes memory /* performData */)
{
upkeepNeeded = (block.timestamp - lastTimeStamp) > interval;
// We don't use the checkData in this example. The checkData is defined when the Upkeep was registered.
}Trong hàm trên, điều kiện để thực thi performUpkeep là thời gian hiện tại với thời gian của lần thực thi trước đó khác nhau hơn một khoảng thời gian nhất định (interval).
Note
Do không dùng
checkDatavàperformDatanên ta inline comment chúng lại.
Một implementation ví dụ của performUpkeep:
function performUpkeep(bytes calldata /* performData */) external override {
if ((block.timestamp - lastTimeStamp) > interval) {
lastTimeStamp = block.timestamp;
counter = counter + 1;
}
// We don't use the performData in this example. The performData is generated by the Automation Node's call to your checkUpkeep function
}Do sử dụng visibility là external, performUpkeep có thể được gọi bởi bất kỳ tài khoản nào ngoài Chainlink contract một cách trực tiếp mà không gọi checkUpkeep trước để kiểm tra. Khi đó, ta cần gọi lại checkUpkeep bên trong hàm thực hiện upkeep chẳng hạn như sau:
(bool upkeepNeeded, ) = checkUpkeep("");
if (!upkeepNeeded) {
revert CustomError();
}