Chain of Responsibility is a behavioral design pattern that lets you pass requests along a chain of handlers. Upon receiving a request, each handler decides either to process the request or to pass it to the next handler in the chain.
Design pattern chain of responsibility sẽ gồm nhiều handler nối tiếp nhau. Mỗi handler sẽ chịu trách nhiệm xử lý một yêu cầu cụ thể. Nếu một handler không thể xử lý thì nó sẽ chuyển tiếp cho handler tiếp theo.
Analogy
Giả sử chúng ta vừa mới mua một linh kiện máy tính mới nhưng lại gặp trục trặc nên quyết định gọi đến bộ phận chăm sóc khách hàng.
Đầu tiên, chúng ta sẽ được tiếp nhận bởi autoresponder (là giọng nói hướng dẫn chúng ta nhấn phím 1 đến 9). Nếu cả 9 phím không giải quyết được vấn đề thì autoresponder sẽ chuyển tiếp qua cho nhân viên hỗ trợ. Và nếu nhân viên hỗ trợ cũng không giúp chúng ta sửa được linh kiện thì họ sẽ chuyển tiếp qua cho kỹ thuật viên.

Đây là một minh họa trong đời sống của chain of responsibility.
Một ví dụ khác: các element ở trong giao diện thường được tổ chức thành dạng cây. Bất cứ khi nào có một sự kiện xảy ra, element đó nếu không xử lý được thì nó sẽ “nổi bọt” lên các element cha.
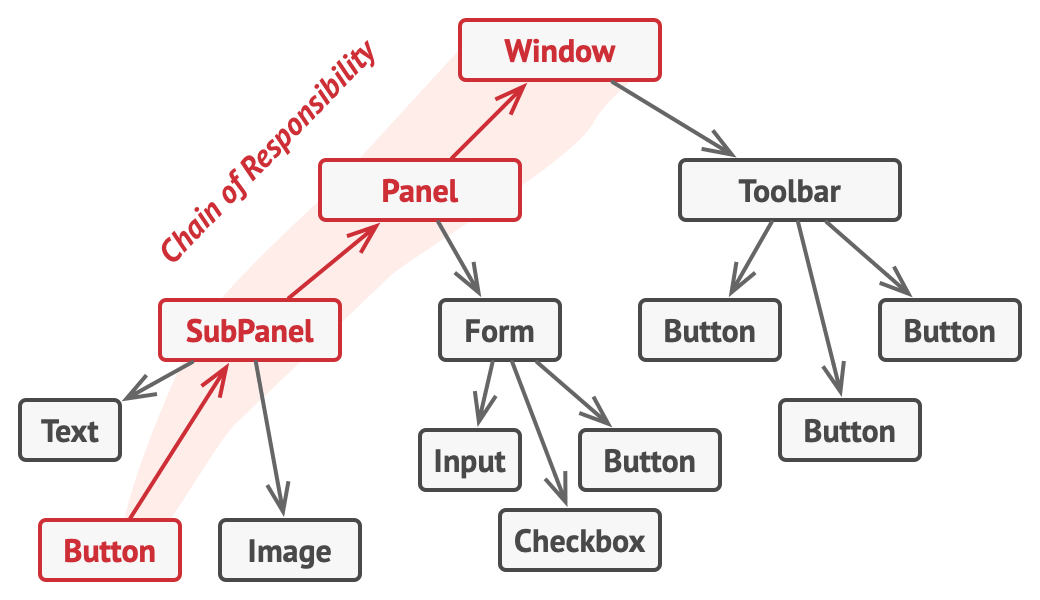
Structure
Cấu trúc của chain of responsibility sẽ bao gồm các thành phần sau:
- Handler: là một interface để các concrete handler kế thừa. Nó thường có một phương thức dùng để xử lý yêu cầu và có thể có một phương thức dùng để thiết lập handler tiếp theo trong chuỗi các handler.
- Base handler (optional): là một abstract class có chứa boilerplate code cho tất cả các handler. Thông thường, base handler sẽ có một thuộc tính lưu handler tiếp theo.
- Concrete handler: là các class chứa các logic chính dùng để xử lý yêu cầu. Mỗi handler cần phải quyết định xem là sẽ xử lý yêu cầu hoặc truyền yêu cầu đó cho handler tiếp theo xử lý.
- Client: kết hợp các handler và gửi yêu cầu.
Minh họa:
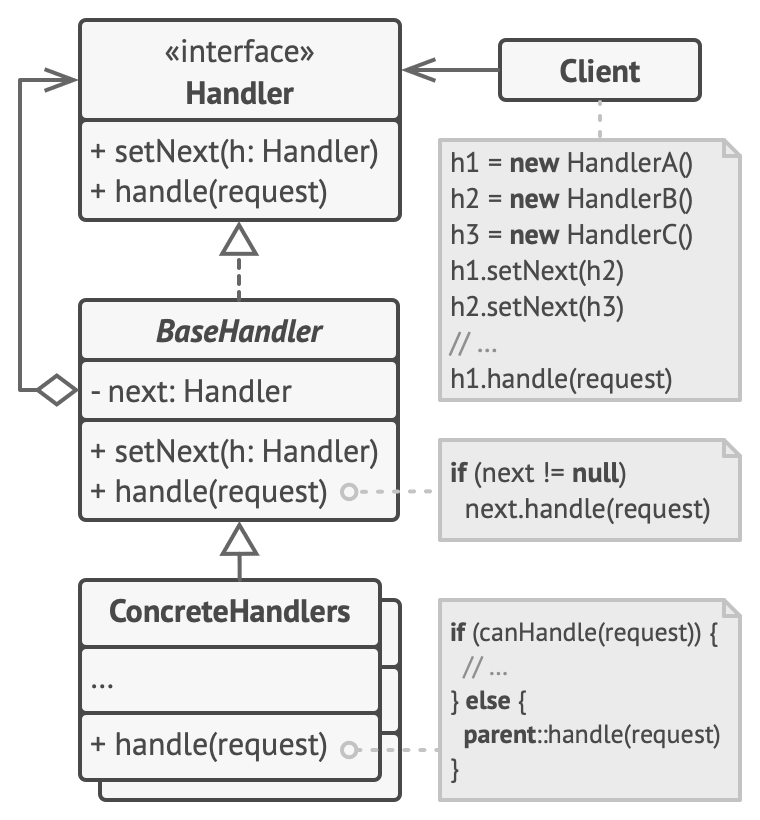
Implementation
Giả sử ta cần xây dựng một hệ thống duyệt yêu cầu nghỉ phép. Người duyệt sẽ bao gồm ba vai trò: giám sát viên, quản lý và giám đốc.
Mỗi vai trò chỉ có thể xử lý một yêu cầu nghỉ phép với số ngày nghỉ tối đa nào đó. Chẳng hạn, giám sát viên chỉ có thể chấp thuận cho nghỉ nếu số ngày nghỉ không quá 3 ngày, quản lý là không quá 5 ngày và giám đốc là hơn 5 ngày.
Trước tiên, ta cần tạo ra một class giúp biểu diễn các yêu cầu xin nghỉ phép:
class LeaveRequest {
private:
int _days;
public:
LeaveRequest(int days) {
_days = days;
}
int getDays() {
return _days;
}
};Base Handler
Tạo ra abstract class Approver vừa là handler interface vừa là base handler như sau:
class Approver {
protected:
Approver* nextApprover = nullptr;
public:
void checkPermission(LeaveRequest request) {
std::cout << "Checking permission for " << className() << "\n";
if (canApprove(request.getDays()))
approve(request);
else if (nextApprover != nullptr)
nextApprover->checkPermission(request);
}
void setNext(Approver* approver) {
nextApprover = approver;
}
private:
virtual std::string className() = 0;
virtual bool canApprove(int numberOfDays) = 0;
virtual void approve(LeaveRequest request) = 0;
};Phân tích:
- Thuộc tính
nextApproverlưu handler tiếp theo. - Phương thức
checkPermissionsẽ giúp handle request còn phương thứcsetNextsẽ giúp thiết lập handler tiếp theo. - Các phương thức còn lại là những phương thức có logic cụ thể tùy thuộc vào từng concrete handler.
Concrete Handlers
Các concrete handler:
Supervisor:
class Supervisor : public Approver {
private:
std::string className() {
return "Supervisor";
}
bool canApprove(int numberOfDays) {
return numberOfDays <= 3;
}
void approve(LeaveRequest request) {
std::cout << "Leave request approved for " << request.getDays() << " days by " << className() << "\n";
}
};Manager:
class Manager : public Approver {
private:
std::string className() {
return "Manager";
}
bool canApprove(int numberOfDays) {
return numberOfDays <= 5;
}
void approve(LeaveRequest request) {
std::cout << "Leave request approved for " << request.getDays() << " days by " << className() << "\n";
}
};Director:
class Director : public Approver {
private:
std::string className() {
return "Director";
}
bool canApprove(int numberOfDays) {
return numberOfDays > 5;
}
void approve(LeaveRequest request) {
std::cout << "Leave request approved for " << request.getDays() << " days by " << className() << "\n";
}
};Building the Handler Chain
Cuối cùng, tạo ra một static method cho phép xây dựng chuỗi các handler như sau:
class LeaveRequestWorkFlow {
public:
static Approver* getApprover() {
Approver* supervisor = new Supervisor();
Approver* manager = new Manager();
Approver* director = new Director();
supervisor->setNext(manager);
manager->setNext(director);
return supervisor;
}
};Usage
Gọi sử dụng như sau:
void TestChainOfResponsibility() {
LeaveRequestWorkFlow::getApprover()->checkPermission(LeaveRequest(2));
std::cout << "---\n";
LeaveRequestWorkFlow::getApprover()->checkPermission(LeaveRequest(5));
std::cout << "---\n";
LeaveRequestWorkFlow::getApprover()->checkPermission(LeaveRequest(7));
std::cout << "---\n";
}Output sẽ là:
Checking permission for Supervisor
Leave request approved for 2 days by Supervisor
---
Checking permission for Supervisor
Checking permission for Manager
Leave request approved for 5 days by Manager
---
Checking permission for Supervisor
Checking permission for Manager
Checking permission for Director
Leave request approved for 7 days by Director
---Applicability
Sử dụng chain of responsibility khi:
- Ứng dụng xử lý nhiều loại request theo nhiều cách.
- Cần thực thi chuỗi các handler theo một thứ tự cụ thể nào đó.
- Khi tập các handler và thứ tự của nó thay đổi trong runtime.
Info
Chain of responsibility được sử dụng để triển khai tính năng middleware trong các ứng dụng web.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Có thể kiểm soát được thứ tự của các request handler | Một số request có thể không được xử lý |
| Single responsibility: tách rời code khởi tạo các thao tác ra khỏi code thực hiện các thao tác | |
| Open/closed: có thể thêm vào các handler mới mà không làm thay đổi client code |